Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Iwatsuki, Teruki; Amano, Yuki; Mie, Hideki
no journal, ,
Hydrochemical changes of groundwater have been observed around the shaft of Mizunami underground research laboratory. Water pressure, pH, and concentrations of calcium, sulphate and bicarbonate ions in groundwater changed in response to shafts sinking. Hydrochemical disturbance seems to reach within the range of surrounding shaft tens of m.
Ishii, Eiichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Oikawa, Teruki; Umeda, Koji; Matsuzaki, Tatsuji*
no journal, ,
K-Ar and FT analyses were carried out on biotite, zircon and apatite from the granitic rocks in Kashiwazima district, western Shikoku in order to reveal the cooling history. These ages suggest rapid cooling of the granitic rocks in the temperature range to 100 C from 300
C from 300 C in 14-13Ma.
C in 14-13Ma.
Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Koji; Nohara, Tsuyoshi; Miwa, Atsushi*; Kurosawa, Hideki*
no journal, ,
Detailed topographical and geological researches for understanding fracture zone structures in fault steps are necessary to estimate the extent of the mechanical damage to basement rocks due to strike-slip fault activities. Our research of the western part of the Atotsugawa Fault in the Hida City, Gifu Prefecture shows that the faults high-angle oblique to the principal direction of the Atotsugawa Fault characteristically occur in fault steps, which effect that the fracture zone increases in width. The Atotsugawa fault, which is one of the Class A active faults, trends ENE-WSW and shows dextral strike-slip displacement. We firstly checked the occurrence of the fault step in the Miyagawa-cho area of the western part of the Atotsugawa Fault by way of aerial photograph interpretation. Then we researched the distribution and feature of fracture zone in the Kawai-cho area where the fault continues lineally and in the Miyagawa-cho area where the fault steps. In the Kawai-cho area, Fault planes mostly strike ENE-WSW to E-W and dip steeply N or S, subparallel to the principal direction of the Atotsugawa Fault. Width of the fracture zone is several tens meters. In the Miyagawa-cho area, NW-SE and N-S strike faults dominantly occur as well as ENE-WSW to E-W strike faults. Width of the fracture zone is more than a hundred meter. Remarkable existence of NW-SE and N-S strike faults distinguishes the fracture zone in the Miyagawa-cho area as that in the Kawai-cho area.
Niwa, Masakazu; Nohara, Tsuyoshi; Mizuochi, Yukihiro*; Tanase, Atsushi*; Kobayashi, Hirohisa*
no journal, ,
The Atera Fault in the eastern part of Gifu Prefecture is a NW-trend active fault and shows sinistral strike-slip displacement. A fracture zone of the Atera Fault, in which granite (Naegi-Agematsu Granite) is in fault contact with welded tuff of the Nohi Rhyolite, is exposed several tens meters in width in Kawaue, Nakatsugawa City. Detailed occurrence of the fracture zone is described in this study to examine the research method to reveal histories of active faults. In the studied fracture zone, fault rocks of the welded tuff origin consist of fault breccia and clay, while those of the granite consist of cataclasite. The fault rocks of the welded tuff origin are more clay-rich than those of the granite origin. Textures of host rocks are more well-preserved in the fault rocks of the granite origin than in those of the the welded tuff origin.
Umeda, Koji; Asamori, Koichi; Negi, Tateyuki*; Ogawa, Yasuo*
no journal, ,
Mesozoic crystalline mountains (Iide Mountains) in a non-volcanic region of the Northeast Japan arc were imaged by wide-band magnetotelluric soundings. A two-dimensional model showed that an anomalous conductive body ( 10 ohm-m) is clearly visible beneath the Iide Mountains. The conductor widens with increasing depth, and extends from the near-surface down to the base of the crust and perhaps into the upper mantle. Considering several signals imaging the presence of crustal magma storage, such as high-temperature regime, hot spring gases with high
10 ohm-m) is clearly visible beneath the Iide Mountains. The conductor widens with increasing depth, and extends from the near-surface down to the base of the crust and perhaps into the upper mantle. Considering several signals imaging the presence of crustal magma storage, such as high-temperature regime, hot spring gases with high  He/
He/ He ratio, thinning of the brittle seismogenic layer and anomalies of low seismic velocity, it is reasonable to suppose that the conductor reflects partial melt and/or high-temperature aqueous fluids in the crust, related to renewed magmatism in the present-day subduction system.
He ratio, thinning of the brittle seismogenic layer and anomalies of low seismic velocity, it is reasonable to suppose that the conductor reflects partial melt and/or high-temperature aqueous fluids in the crust, related to renewed magmatism in the present-day subduction system.
Mizuno, Takashi; Iwatsuki, Teruki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Mizuno, Takashi; Metcalfe, R.*; Mie, Hideki; Iwatsuki, Teruki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nohara, Tsuyoshi; Nakata, Takashi*; Shimada, Koji; Niwa, Masakazu; Kinoshita, Hirohisa; Sagiya, Takeshi*
no journal, ,
Features of subsurface active faults are studied using data of the damaging earthquake, geological structure and diastrophism. The hypocenter of the damaging earthquakes distribute around the Quaternary volcanoes and the active faults. The direction of strike and displacement of the active faults and the earthquake faults of the damaging earthquakes occurred around the active faults are almost same. The dispersion of the deformation of the mylonite zone related to geological condition may be one of the indicators of generation of subsurface active fault.
 gas corresponding to attitudes of incohesive fault rock layers
gas corresponding to attitudes of incohesive fault rock layersShimada, Koji; Niwa, Masakazu; Nohara, Tsuyoshi; Tanaka, Hidemi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Asamori, Koichi; Umeda, Koji; Negi, Tateyuki*; Ogawa, Yasuo*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Mashima, Hidehisa
no journal, ,
Basaltic andesites distributed at Saga-Futagoyama, northwest Kyushu, southwest Japan are high magnesium andesites (HMA) originally equilibrated with Fe-rich mantle. The reasonsfor thinking so are twofold. The andesites contain orthopyroxene phenocrysts with Mg/(Mg+Fe)=0.8. The bulk rock Mg-Fe-Ni compositions suggest that the andesite magmas could equilibrate with mantle olivines. Hydrous components derived from the subducting slab played an insignificant role in the genesis of the Saga-Futagoyama HMA magmas. Lines of evidence for this interpretation are following. KD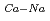 =1.25 between plagioclase and melt suggests that the HMA magmas originally contain less than 1.8 wt.% H
=1.25 between plagioclase and melt suggests that the HMA magmas originally contain less than 1.8 wt.% H O. Nb/La of the Saga-Futagoyama samples is higher than one and has an insignificant correlation with SiO
O. Nb/La of the Saga-Futagoyama samples is higher than one and has an insignificant correlation with SiO . All of previously reported mantle xenoliths from NW Kyushu have anhydrous mineral assemblages. The subducted Philippine Sea plate does not extend to NW Kyushu. Normative Jd+CaTs-Ol-Qz compositions of the HMA suggest that they were separated from their source mantle at 0.5 GPa. This abnormally low pressure partial melting would be caused by the weakening of the lithospheric mantle beneath the Karatsu-Sasebo basin during its subsidence and uplift.
. All of previously reported mantle xenoliths from NW Kyushu have anhydrous mineral assemblages. The subducted Philippine Sea plate does not extend to NW Kyushu. Normative Jd+CaTs-Ol-Qz compositions of the HMA suggest that they were separated from their source mantle at 0.5 GPa. This abnormally low pressure partial melting would be caused by the weakening of the lithospheric mantle beneath the Karatsu-Sasebo basin during its subsidence and uplift.
Mashima, Hidehisa; Tajima, Toshihiko*
no journal, ,
High magnesium andesites (HMAs) with island arc geochemical signatures are distributed in Nagasaki, Northwest Kyushu, Southwest Japan. The genesis of the Nagasaki HMAs cannot be explained by current flux melting models for HMA magmas since mantle xenoliths from NW Kyushu suggests that the NW Kyushu mantle is anhydrous. Normative Jd+CaTs-Ol-Qz compositions of the HMAs suggest that they were separated from their source mantle at 0.5 GPa. This abnormally low pressure partial melting would have been caused by the large contrast of lithospheric strength between the land area composed of the Nagasaki metamorphic rocks and the sea area where sedimentary basins have been formed. The large contrast of lithospheric strength would have concentrated mantle upwelling at the boundary between the land and the sea areas. In the genesis of the Nagasaki HMA magmas, the subduction of the Philippine Sea plate would habe played not as the source of hydrous components but as the driving force of strike-slip tectonics in NW Kyushu.
Nakajima, Takahiro; Kunitomo, Takahiro; Nagao, Hiromichi; Kumazawa, Mineo
no journal, ,
We have developed and tested an electromagnetic sounding method, called EM-ACROSS (ElectroMagnetic - Accurately Controlled Rountinely Operated Signal System). We prepared two horizontal current dipole sources for two independent vector components of transmitting signal, in order to obtain the information on the anisotropy and lateral heterogeneity through the dependence of signal propagattion on azimuth and polarization. We report results of the observation and the analysis of the tensor transfer function obtained by the new observation system.
 He/
He/ He ratios in gases in Japan
He ratios in gases in JapanKanazawa, Sunao; Asamori, Koichi; Umeda, Koji; Shimada, Koji
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Takahashi, Kazuharu; Niizato, Tadafumi; Yasue, Kenichi; Amo, Miki*; Suzuki, Noriyuki*
no journal, ,
This article presents the adapted results of the estimation method of erosion and uplifting based on mineralogy and organic geochemical characters of the Neogene siliceous rock (Wakkanai and Koitoi Formations) in Horonobe in succession to last year's article(Takahashi et al., 2005a).
Kunitomo, Takahiro; Kumazawa, Mineo
no journal, ,
We have started the automated routine transmission of the accurately controlled elastic wave signals by the seismic ACROSS transmitter at Tono mine (Toki-shi, Gifu) from Oct. 2002, and continuous observations have been executed for more than three years, in order to establish a routine technology of the next generation for the structural exploration and active monitoring of the Earth's interiors by seismic waves. We report mainly the results obtained by the experiments.
Yasue, Kenichi; Niizato, Tadafumi; Chiba, Akihiko*
no journal, ,
Information about shallow subsurface geological structures, about 10m in depth, is useful for the estimation of a detailed position and an activity of fault, and discovery of concealed fault, and so on. We carried out the GPR (ground penetration radar) exploration to clarify the subsurface geological structure around the area where the Omagari-Toyotomi Fault was estimated. In addition, we carried out an interpretation of aerial photograph, topographical and geological investigations, and drawing up of detail counter maps. Study sites are Kaishin and Hokushin districts in the Horonobe Town, northern Hokkaido. We used the GPR with antennas of 25 MHz and 100 MHz frequencies on the alluvial surface and the lower river terrace surface. GPR profiles show the thickness of the alluvium and the terrace deposit, the distribution of the basement rock, and the structure in the alluvium. The results of this study show that GPR exploration is an effective tool to investigate the shallow subsurface geological structure in the area where the fault topography would be altered by periglacial phenomena and man-caused effects.
Takeuchi, Shinji
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kumazawa, Mineo; Ogawa, Katsuro*; Fujii, Naoyuki; Yamaoka, Koshun; Kunitomo, Takahiro; Nakajima, Takahiro; Tsuruga, Kayoko; Hasada, Yoko; Kasahara, Junzo; Shigeta, Naotaka; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English